GeoTIFF
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
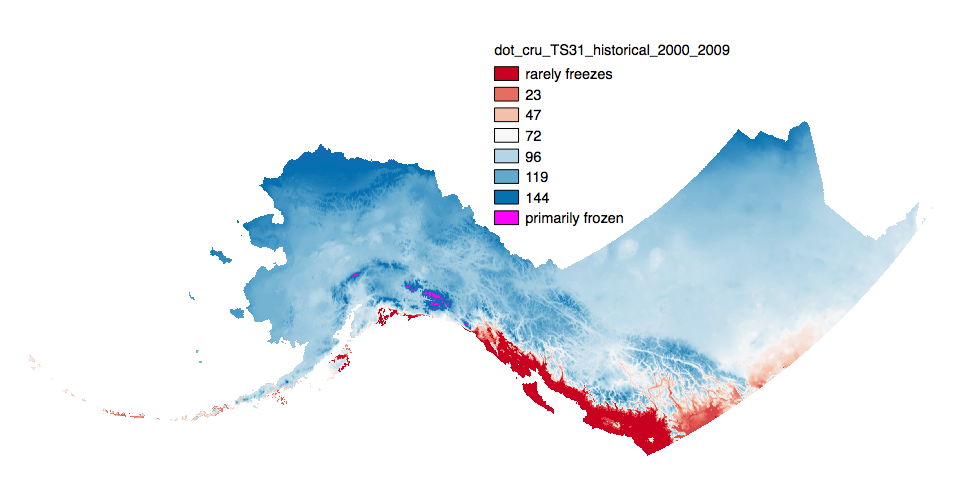
This set of files includes downscaled historical estimates of decadal means of annual day of freeze or thaw (ordinal day of the year), and length of growing season (numbers of days, 0-365) for each decade from 1910 - 2006 (CRU TS 3.0) or 2009 (CRU TS 3.1) at 2x2 kilometer spatial resolution. Each file represents a decadal mean of an annual mean calculated from mean monthly data. **Day of freeze or thaw units are ordinal day 15-350 with the below special cases.** *Day of Freeze (DOF)* `0` = Primarily Frozen `365` = Rarely Freezes *Day of Thaw (DOT)* `0` = Rarely Freezes `365` = Primarily Frozen *Length of Growing Season (LOGS)* is simply the number of days between the DOT and DOF. ---- The spatial extent includes Alaska, the Yukon Territories, British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. Each set of files originates from the Climatic Research Unit (CRU, http://www.cru.uea.ac.uk/) TS 3.0 or 3.1 dataset. TS 3.0 extends through December 2006 while 3.1 extends to December 2009. **Day of Freeze, Day of Thaw, Length of Growing Season calculations:** Estimated ordinal days of freeze and thaw are calculated by assuming a linear change in temperature between consecutive months. Mean monthly temperatures are used to represent daily temperature on the 15th day of each month. When consecutive monthly midpoints have opposite sign temperatures, the day of transition (freeze or thaw) is the day between them on which temperature crosses zero degrees C. The length of growing season refers to the number of days between the days of thaw and freeze. This amounts to connecting temperature values (y-axis) for each month (x-axis) by line segments and solving for the x-intercepts. Calculating a day of freeze or thaw is simple. However, transitions may occur several times in a year, or not at all. The choice of transition points to use as the thaw and freeze dates which best represent realistic bounds on a growing season is more complex. Rather than iteratively looping over months one at a time, searching from January forward to determine thaw day and from December backward to determine freeze day, stopping as soon as a sign change between two months is identified, the algorithm looks at a snapshot of the signs of all twelve mean monthly temperatures at once, which enables identification of multiple discrete periods of positive and negative temperatures. As a result more realistic days of freeze and thaw and length of growing season can be calculated when there are idiosyncrasies in the data.
-
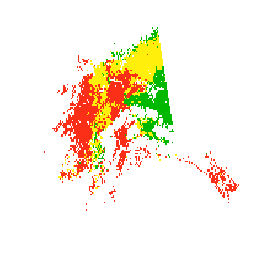
This dataset is the product of a climate-driven model of beetle survival and reproduction in Alaska. We used that model to create this dataset of landscape-level “risk” of the climatic component of beetle infestation across the forested areas of Alaska. This risk component can best be applied as protection of the landscape offered by the climate and is categorized as high, medium, and low. It does not consider other major factors, such as existing beetle and predator populations or forest susceptibility. We computed these values over one historical period (1988-2017) using Daymet data, and three future periods (2010-2039, 2040-2069, 2070-2099) using four statistically downscaled global climate model projections, each run under two plausible greenhouse gas futures (RCP 4.5 and 8.5).
-
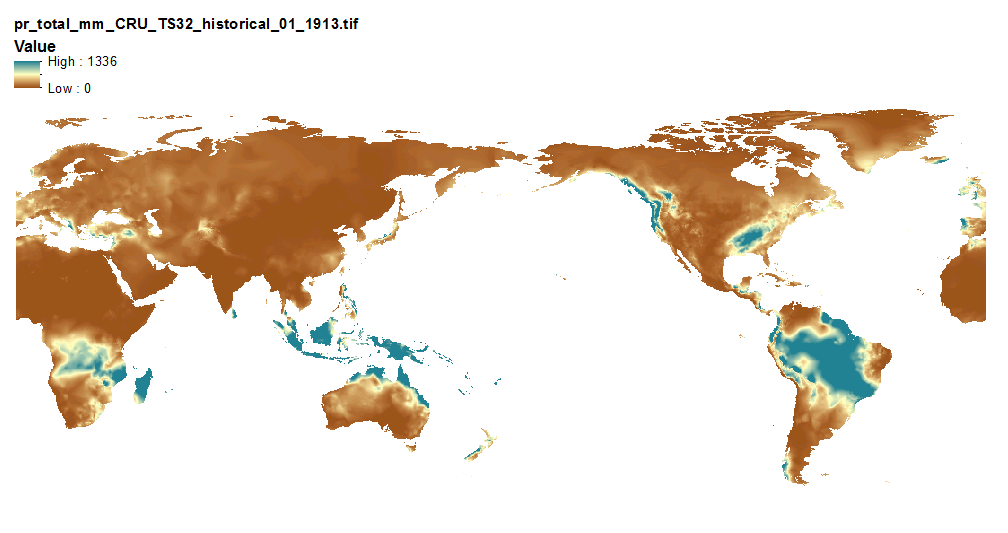
This set of files includes downscaled historical estimates of monthly total precipitation (in millimeters, no unit conversion necessary, rainwater equivalent) from 1901 - 2013 (CRU TS 3.22) at 10 min x 10 min spatial resolution with global coverage. The downscaling process utilizes CRU CL v. 2.1 climatological datasets from 1961-1990.
-

This dataset includes 42,120 GeoTIFFs (spatial resolution: 12 km) that represent decadal (15 decades between 1950-2099) means of monthly summaries of the following variables (units, abbreviations and case match those used in the source daily resolution dataset). There are three distinct groups of variables: Meteorological, Water State, and Water Flux. Meteorological Variables - tmax (Maximum daily 2-m air temperature, °C) - tmin (Minimum daily 2-m air temperature, °C) - pcp (Daily precipitation, mm per day) Water State Variables - SWE (Snow water equivalent, mm) - IWE (Ice water equivalent, mm) - SM1 (Soil moisture layer 1: surface to 0.02 m depth, mm) - SM2 (Soil moisture layer 2: 0.02 m to 0.97 m depth, mm) - SM3 (Soil moisture layer 3: 0.97 m to 3.0 m depth, mm) Water Flux Variables - RUNOFF (Surface runoff, mm per day) - EVAP (Actual evapotranspiration, mm per day) - SNOW_MELT (Snow melt, mm per day) - GLACIER_MELT (Ice melt, mm per day) Monthly summary functions, or how the daily frequency source data are condensed into a single monthly value, are as follows: - Sum: pcp, SNOW_MELT, EVAP, GLACIER_MELT, RUNOFF - Mean: tmin, tmax, SM1, SM2, SM3 - Maximum: IWE, SWE The model-scenario combinations used to represent various plausible climate futures are: - ACCESS1-3, RCP 4.5 - ACCESS1-3, RCP 8.5 - CanESM2, RCP 4.5 - CanESM2, RCP 8.5 - CCSM4, RCP 4.5 - CCSM4, RCP 8.5 - CSIRO-Mk3-6-0, RCP 4.5 - CSIRO-Mk3-6-0, RCP 8.5 - GFDL-ESM2M, RCP 4.5 - GFDL-ESM2M, RCP 8.5 - HadGEM2-ES, RCP 4.5 - HadGEM2-ES, RCP 8.5 - inmcm4, RCP 4.5 - inmcm4, RCP 8.5 - MIROC5, RCP 4.5 - MIROC5, RCP 8.5 - MPI-ESM-MR, RCP 4.5 - MPI-ESM-MR, RCP 8.5 - MRI-CGCM3, RCP 4.5 - MRI-CGCM3, RCP 8.5 The .zip files that are available for download are organized by variable. One .zip file has all the models and scenarios and decades and months for that variable. Each GeoTIFF file has a naming convention like this: {climate variable}_{units}_{model}_{scenario}_{month abbreviation}_{summary function}_{decade start}-{decade end}_mean.tif Each GeoTIFF has a 12 km by 12 km pixel size, and is projected to EPSG:3338 (Alaska Albers).
-
This dataset consists of spatial representations of vegetation types produced through summarization of ALFRESCO model outputs. These specific outputs are from the Integrated Ecosystem Model (IEM) project, AR5/CMIP5 climate inputs (IEM Generation 2). ALFRESCO outputs were summarized over three future eras (2010-2039, 2040-269, 2070-2099) and a historical era (1950-2008). Both the proportions of all possible vegetation types and the modal vegetation type (most common type over a given era) are available as sub-datasets. Each are summarized over two future emissions scenarios for five CMIP5 models.
-
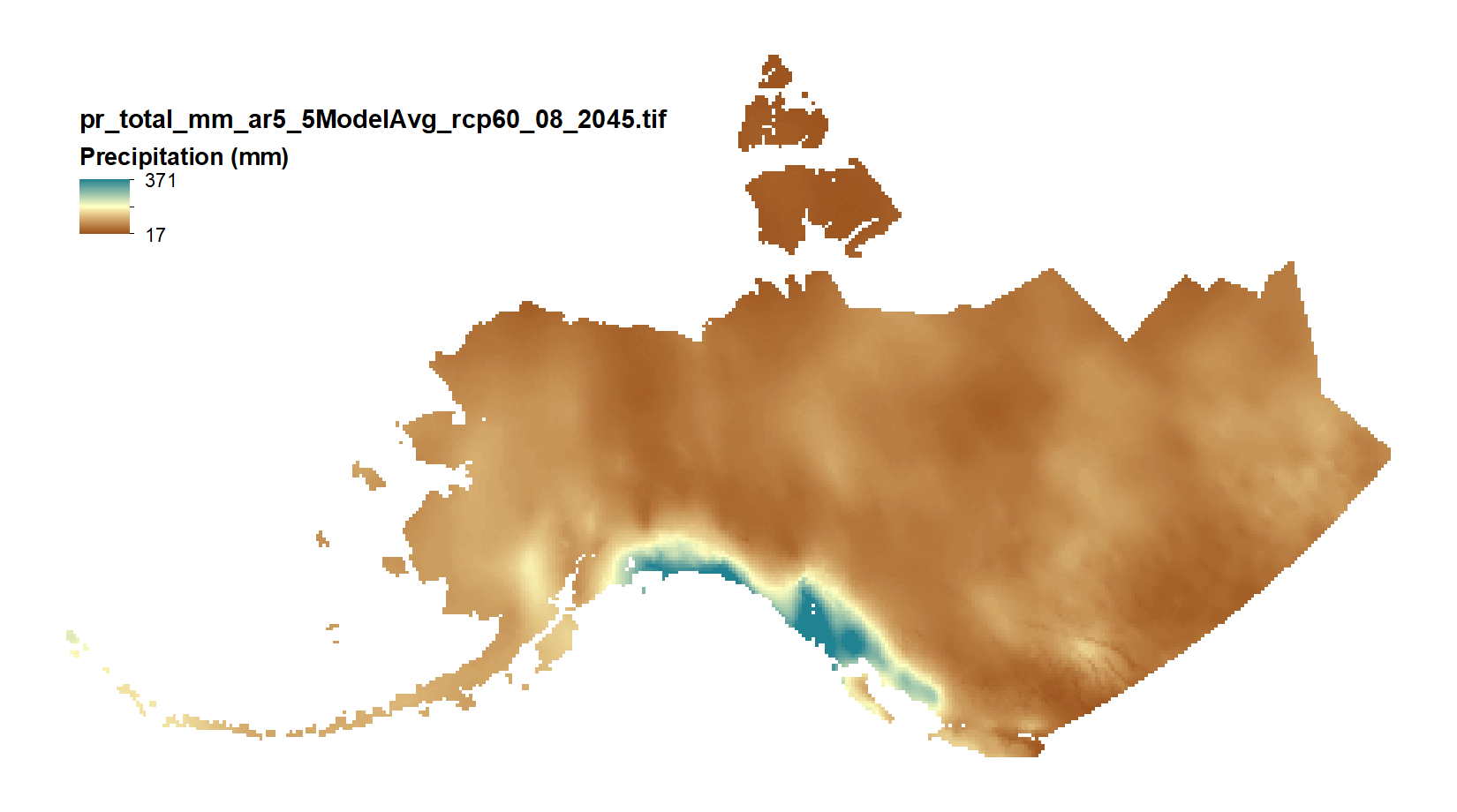
This set of files includes downscaled projections of monthly totals, and derived annual, seasonal, and decadal means of monthly total precipitation (in millimeters, no unit conversion necessary) from Jan 2006 - Dec 2100 at 771x771 meter spatial resolution. Each set of files originates from one of five top ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RPCs, or is calculated as a 5 Model Average. The downscaling process utilizes PRISM climatological datasets from 1971-2000. Brief descriptions of the datasets: Monthly precipitation totals: The total precipitation, in mm, for the month. For Decadal outputs: 1. Decadal Average Total Monthly Precipitation: 10 year average of total monthly precipitation. Example: All January precipitation files for a decade are added together and divided by ten. 2. Decadal Average Seasonal Precipitation Totals: 10 year average of seasonal precipitation totals. Example: MAM seasonal totals for every year in a decade are added together and divided by ten. 3. Decadal Average Annual Precipitation Totals: 10 year average of annual cumulative precipitation. For seasonal means, the four seasons are referred to by the first letter of 3 months making up that season: * `JJA`: summer (June, July, August) * `SON`: fall (September, October, November) * `DJF`: winter (December, January, February) * `MAM`: spring (March, April, May) Please note that these maps represent climatic estimates only. While we have based our work on scientifically accepted data and methods, uncertainty is always present. Uncertainty in model outputs tends to increase for more distant climatic estimates from present day for both historical summaries and future projections.
-
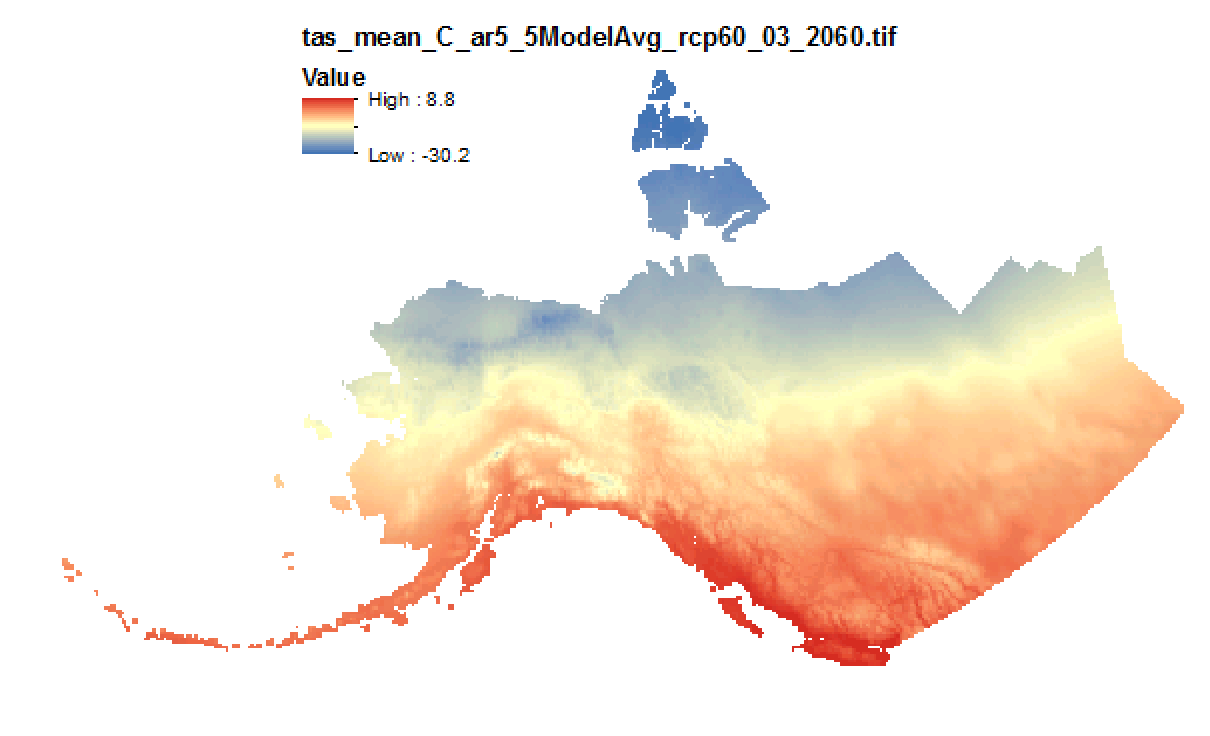
This set of files includes downscaled projected estimates of monthly temperature (in degrees Celsius, no unit conversion necessary) from 2006-2300* at 15km x 15km spatial resolution. They include data for Alaska and Western Canada. Each set of files originates from one of five top ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RCPs, or is calculated as a 5 Model Average. *Some datasets from the five models used in modeling work by SNAP only have data going out to 2100. This metadata record serves to describe all of these models outputs for the full length of future time available. The downscaling process utilizes CRU CL v. 2.1 climatological datasets from 1961-1990 as the baseline for the Delta Downscaling method.
-
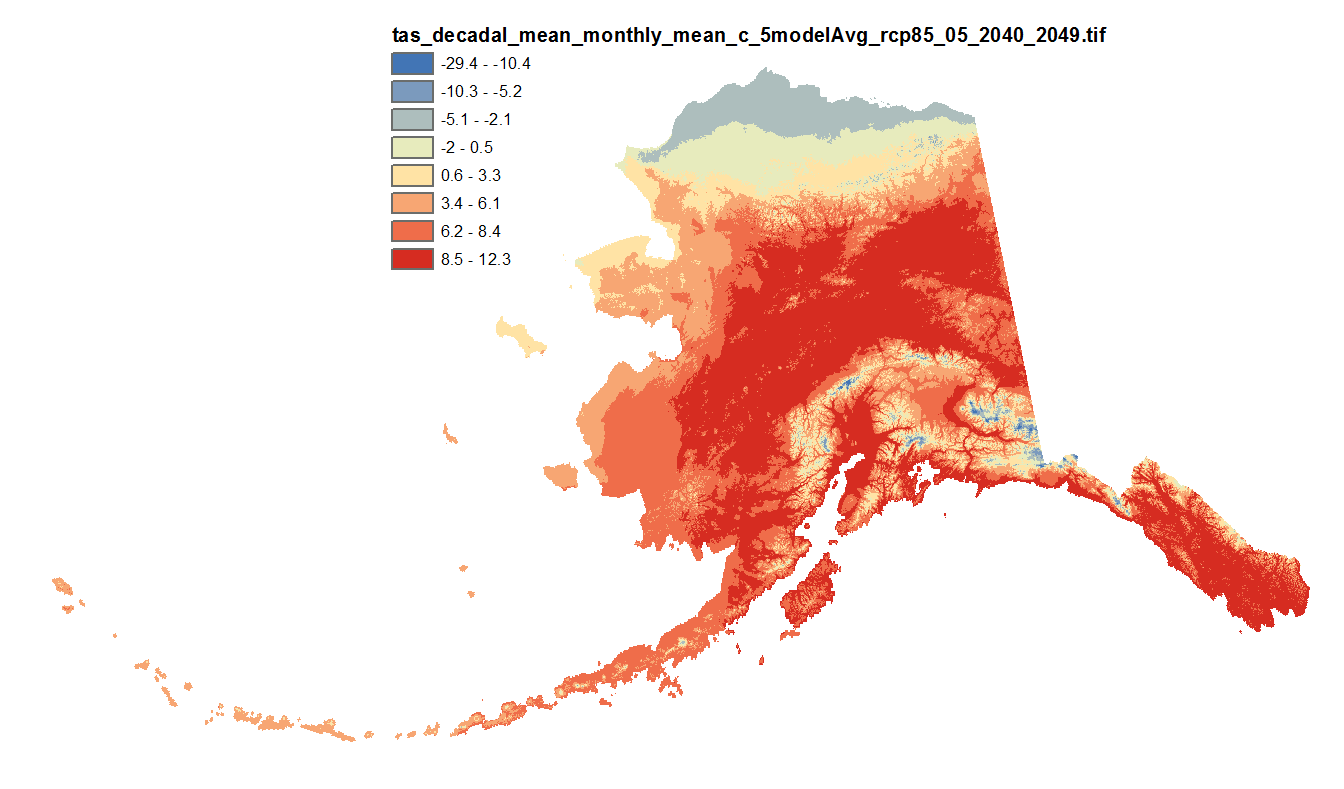
This set of files includes downscaled projections of monthly means, and derived annual, seasonal, and decadal means of monthly mean temperatures (in degrees Celsius, no unit conversion necessary) from Jan 2006 - Dec 2100 at 771x771 meter spatial resolution. For seasonal means, the four seasons are referred to by the first letter of 3 months making up that season: * `JJA`: summer (June, July, August) * `SON`: fall (September, October, November) * `DJF`: winter (December, January, February) * `MAM`: spring (March, April, May) The downscaling process utilizes PRISM climatological datasets from 1971-2000. Each set of files originates from one of five top-ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RCPs or is calculated as a 5 Model Average.
-
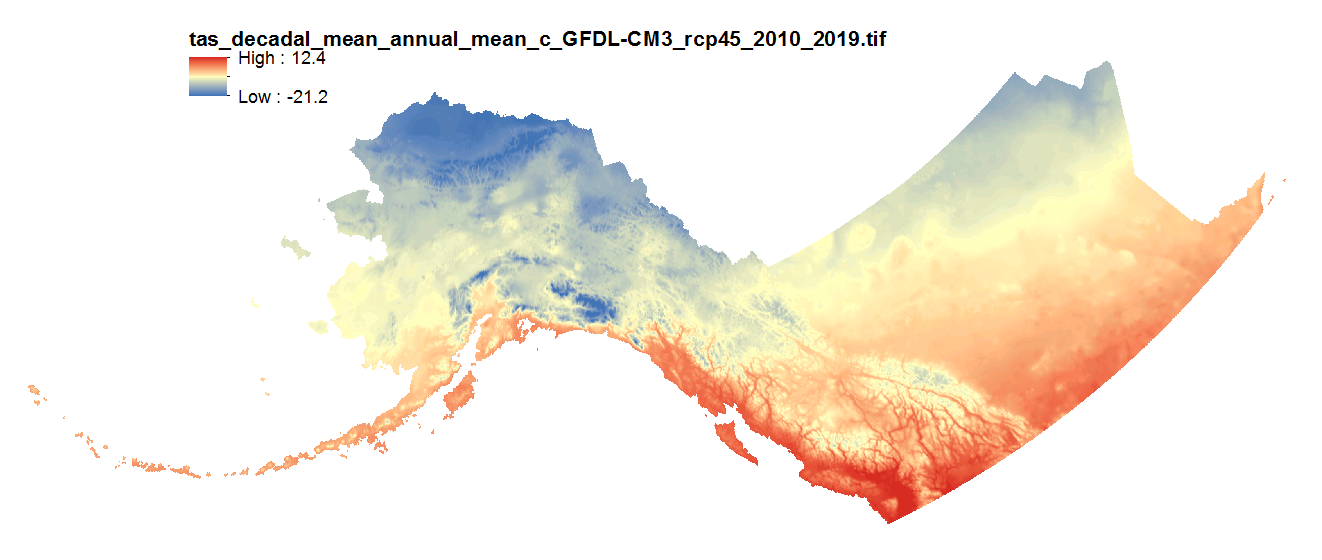
This set of files includes downscaled projections of monthly average, minimum, and maximum temperature and derived annual, seasonal, and decadal means of monthly average temperature (in degrees Celsius, no unit conversion necessary) from Jan 2006 - Dec 2100 at 2km x 2km spatial resolution across Alaska and parts of Canada. For seasonal means, the four seasons are referred to by the first letter of 3 months making up that season: * `JJA`: summer (June, July, August) * `SON`: fall (September, October, November) * `DJF`: winter (December, January, February) * `MAM`: spring (March, April, May) Each set of files originates from one of five top ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RPCs, or is calculated as a 5 Model Average. The downscaling process utilizes PRISM climatological datasets from 1961-1990. Please note that these maps represent climatic estimates only. While we have based our work on scientifically accepted data and methods, uncertainty is always present. Uncertainty in model outputs tends to increase for more distant climatic estimates from present day for both historical summaries and future projections.
-
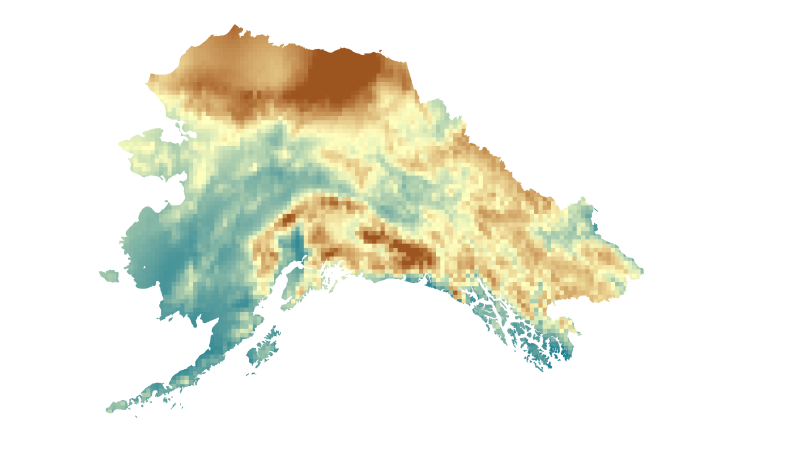
This set of files includes downscaled future projections of vapor pressure (units=hPa) at a 1km spatial scale. This data has been prepared as model input for the Integrated Ecosystem Model (IEM). There can be errors or serious limitations to the application of this data to other analyses. The data constitute the result of a downscaling procedure using 2 General Circulation Models (GCM) from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project 5 (CMIP5) for RCP 8.5 scenario (2006-2100) monthly time series and Climatic Research Unit (CRU) TS2.0 (1961-1990,10 min spatial resolution) global climatology data. Please note that this data is used to fill in a gap in available data for the Integrated Ecosystem Model (IEM) and does not constitute a complete or precise measurement of this variable in all locations. RCPs: 8.5 Centers, Model Names, Versions, and Acronyms: National Center for Atmospheric Research,Community Earth System Model 4,NCAR-CCSM4 Meteorological Research Institute,Coupled General Circulation Model v3.0,MRI-CGCM3 Methods of creating downscaled relative humidity data: 1. The GCM input data are distributed as relative humidity along with the CRU CL 2.0, therefore no conversion procedure was necessary before beginning the downscaling procedure. 2. Proportional Anomalies generated using the 20c3m Historical relative humidity data 1961-1990 climatology and the projected relative humidity data (2006-2100). 3. These proportional anomalies are interpolated using a spline interpolation to a 10min resolution grid for downscaling with the CRU CL 2.0 Relative Humidity Data. 4. The GCM proportional anomalies are multiplied by month to the baseline CRU CL 2.0 10min relative humidity climatology for the period 1961-1990. Creating a downscaled relative humidity projected time series 2006-2100. 5. Due to the conversion procedure and the low quality of the input data to begin with, there were values that fell well outside of the range of acceptable relative humidity (meaning that there were values >100 percent), these values were re-set to a relative humidity of 95 at the suggestion of the researchers involved in the project. It is well known that the CRU data is spotty for Alaska and the Circumpolar North, due to a lack of weather stations and poor temporal coverage for those stations that exist. 6. The desired output resolution for the AIEM modeling project is 1km, so the newly created downscaled time series is resampled to this resolution using a standard bilinear interpolation resampling procedure. 7. The final step was to convert the downscaled relative humidity data to vapor pressure using the calculation below, which uses a downscaled temperature data set created utilizing the same downscaling procedure. EQUATION: saturated vapor pressure = 6.112 x exp(17.62 x temperature/(243.12+temperature)) vapor pressure = (relative humidity x saturated vapor pressure)/100
 SNAP GeoNetwork
SNAP GeoNetwork