Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
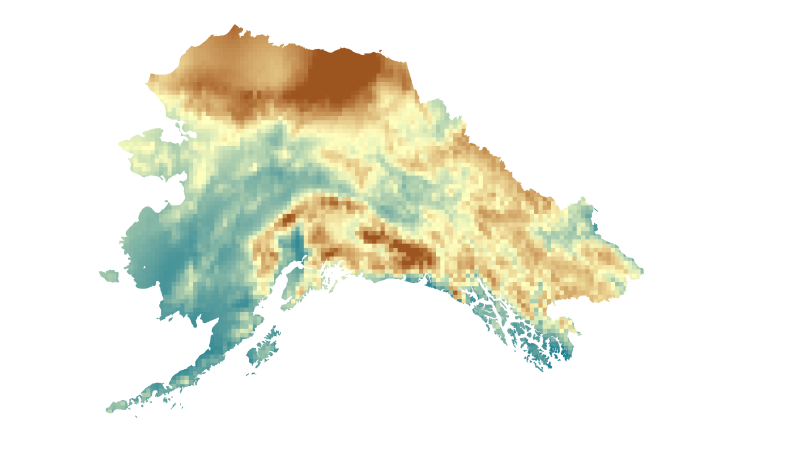
This set of files includes downscaled future projections of vapor pressure (units=hPa) at a 1km spatial scale. This data has been prepared as model input for the Integrated Ecosystem Model (IEM). There can be errors or serious limitations to the application of this data to other analyses. The data constitute the result of a downscaling procedure using 2 General Circulation Models (GCM) from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project 5 (CMIP5) for RCP 8.5 scenario (2006-2100) monthly time series and Climatic Research Unit (CRU) TS2.0 (1961-1990,10 min spatial resolution) global climatology data. Please note that this data is used to fill in a gap in available data for the Integrated Ecosystem Model (IEM) and does not constitute a complete or precise measurement of this variable in all locations. RCPs: 8.5 Centers, Model Names, Versions, and Acronyms: National Center for Atmospheric Research,Community Earth System Model 4,NCAR-CCSM4 Meteorological Research Institute,Coupled General Circulation Model v3.0,MRI-CGCM3 Methods of creating downscaled relative humidity data: 1. The GCM input data are distributed as relative humidity along with the CRU CL 2.0, therefore no conversion procedure was necessary before beginning the downscaling procedure. 2. Proportional Anomalies generated using the 20c3m Historical relative humidity data 1961-1990 climatology and the projected relative humidity data (2006-2100). 3. These proportional anomalies are interpolated using a spline interpolation to a 10min resolution grid for downscaling with the CRU CL 2.0 Relative Humidity Data. 4. The GCM proportional anomalies are multiplied by month to the baseline CRU CL 2.0 10min relative humidity climatology for the period 1961-1990. Creating a downscaled relative humidity projected time series 2006-2100. 5. Due to the conversion procedure and the low quality of the input data to begin with, there were values that fell well outside of the range of acceptable relative humidity (meaning that there were values >100 percent), these values were re-set to a relative humidity of 95 at the suggestion of the researchers involved in the project. It is well known that the CRU data is spotty for Alaska and the Circumpolar North, due to a lack of weather stations and poor temporal coverage for those stations that exist. 6. The desired output resolution for the AIEM modeling project is 1km, so the newly created downscaled time series is resampled to this resolution using a standard bilinear interpolation resampling procedure. 7. The final step was to convert the downscaled relative humidity data to vapor pressure using the calculation below, which uses a downscaled temperature data set created utilizing the same downscaling procedure. EQUATION: saturated vapor pressure = 6.112 x exp(17.62 x temperature/(243.12+temperature)) vapor pressure = (relative humidity x saturated vapor pressure)/100
-
This dataset consists of observed and modeled wind data at an hourly temporal resolution for 67 communities in Alaska. Hourly ASOS/AWOS wind data (speed and direction) available via the Iowa Environmental Mesonet AK ASOS network were accessed and assessed for completeness, and 67 of those stations were determined to be sufficiently complete for climatological analysis. Those data were cleaned to produce regular hourly data, and adjusted via a combination of changepoint analysis and quantile mapping to correct for potential changes in sensor location and height. Historical (ERA-Interim reanalysis) and projected (GFDL-CM3 and NCAR-CCSM4) outputs from a dynamical downscaling effort were extracted at pixels intersecting the chosen communities and were bias-corrected using the cleaned station data. This bias-corrected historical and projected data along with cleaned station data make up the entirety of this dataset as a collection of CSV files, for each combination of community and origin (station or model name).
-
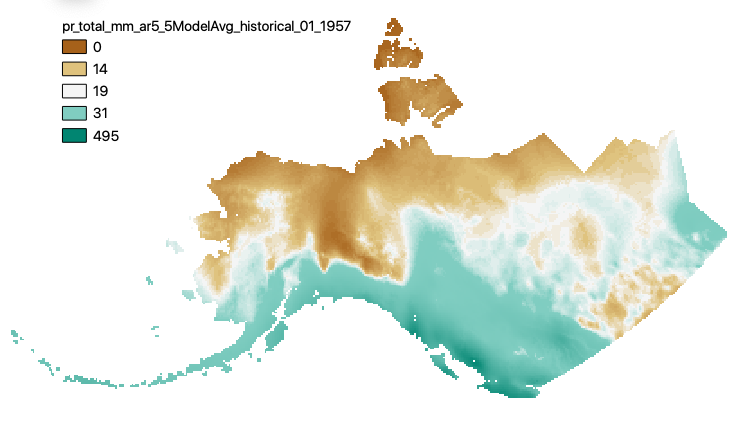
This set of files includes downscaled historical estimates of monthly total precipitation (in mm, no unit conversion necessary) from 1901 - 2005, at 15km x 15km spatial resolution. They include data for Alaska and Western Canada. Each set of files originates from one of five top ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RCPs, or is calculated as a 5 Model Average. These outputs are from the Historical runs of the GCMs. The downscaling process utilizes CRU CL v. 2.1 climatological datasets from 1961-1990 as the baseline for the Delta Downscaling method.
-
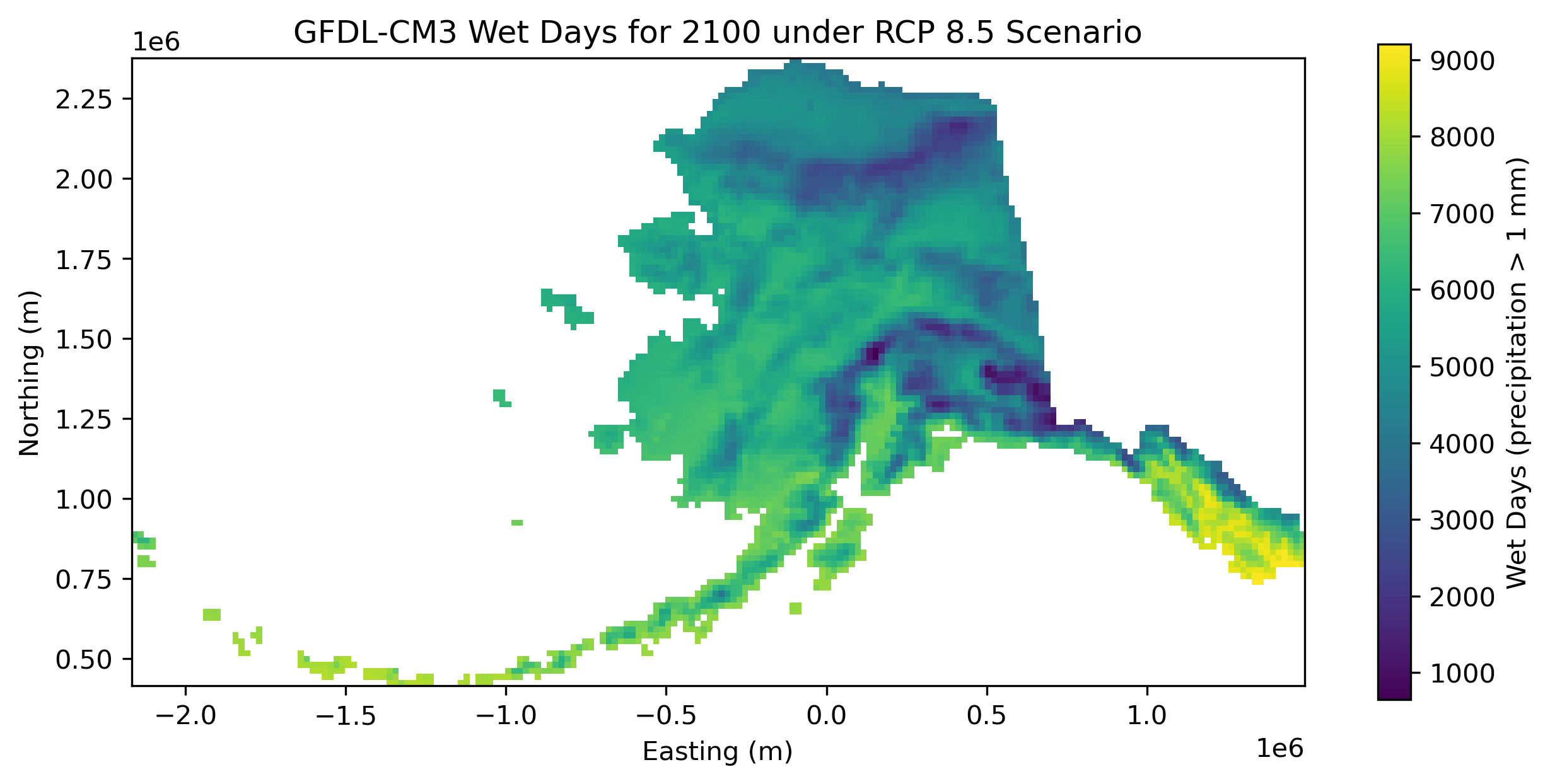
This dataset consists of single band GeoTIFFs containing total annual counts of wet days for each year from 1980-2100 for one downscaled reanalysis (ERA-Interim, 1980-2015) and two downscaled CMIP5 global climate models driven under the RCP 8.5 baseline emissions scenario (NCAR-CCSM4 and GFDL-CM3, 2006-2100), all derived from the same dynamical downscaling effort using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model (Version 3.5). A day is counted as a "wet day" if the total precipitation for that day is 1 mm or greater.
-
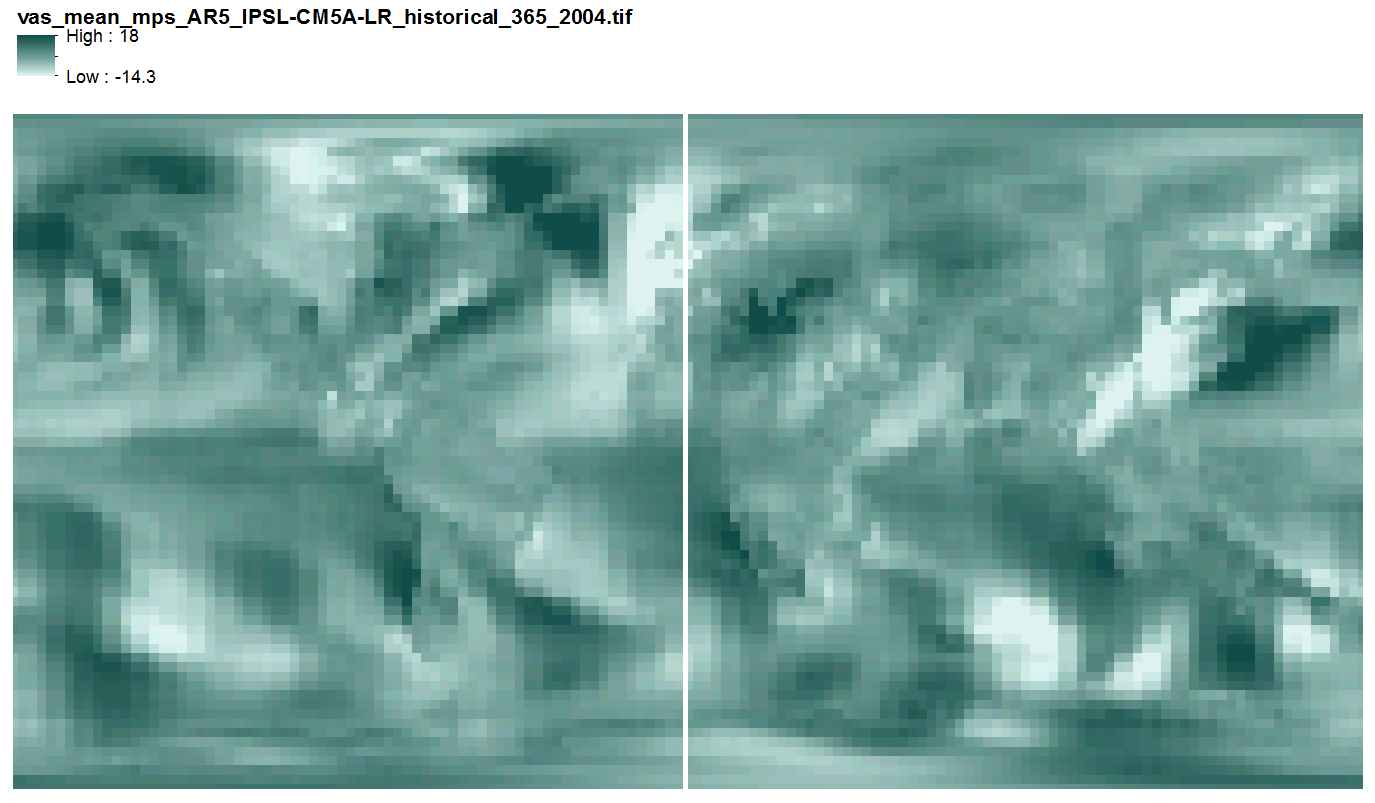
This data includes quantile-mapped historical and projected model runs of AR5 daily mean near surface wind velocity (m/s) for each day of every year from 1958 - 2100 at 2.5 x 2.5 degree spatial resolution across 3 AR5 models. They are 365 multi-band geotiff files, one file per year, each band representing one day of the year, with no leap years.
-
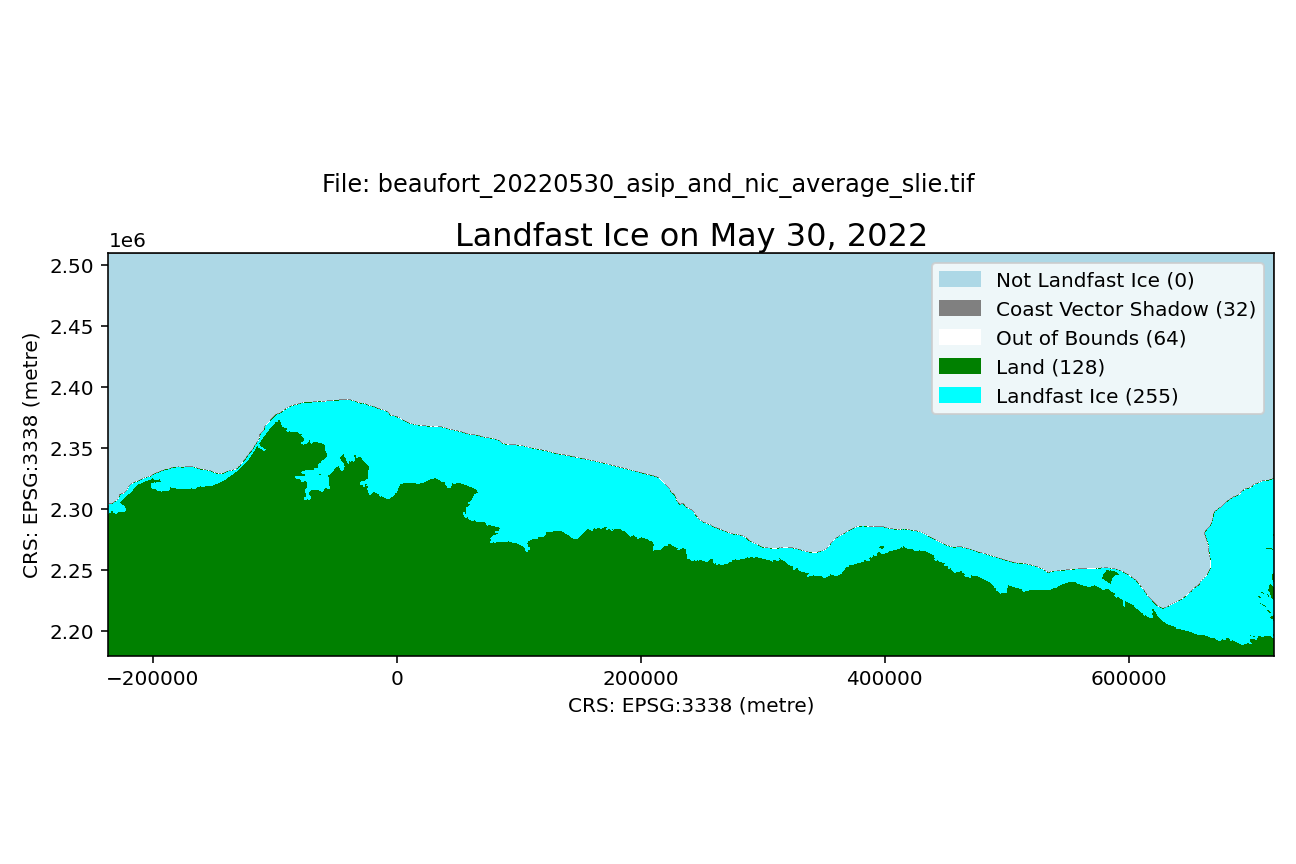
A dataset of landfast ice extent along the Alaska coast of the Beaufort Sea and adjacent waters in Canada spanning the winters of 1996-2023. Landfast ice extent is defined as the area between the coast and the seaward landfast ice edge (SLIE), meaning that small areas of open water than can form at the coast springtime will not be represented. Spatial resolution is 100 m. Compilation of the dataset is described in detail by Mahoney et al (2024). In brief, it is derived from three sources: From 1996-2008, the dataset is derived from analysis of sequential synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images from the RadarSAT and EnviSAT constellations, as described by Mahoney et al (2014); From 2008-2023, the data represent an average landfast extent identified in ice charts from the U.S. National Weather Service Alaska Sea Ice Program (ASIP) and the U.S. National Ice Center (NIC). Within each GeoTIFF file there are 5 different pixel values representing different characteristics: 0 - Not Landfast Ice 32 - Coast Vector Shadow 64 - Out of Bounds 128 - Land 255 - Landfast ice The file naming convention is as follows: beaufort_$YYYYMMDD_$source_slie.tif For example, the name beaufort_20170302_asip_and_nic_average_slie.tif indicates the file represents data for March 2, 2017 and that the data is derived from an average of the ASIP and NIC data sources. These data were updated on August 21, 2025 to rectify the omission of some NIC chart data sources for the 2017-18 and 2018-19 seasons.
-
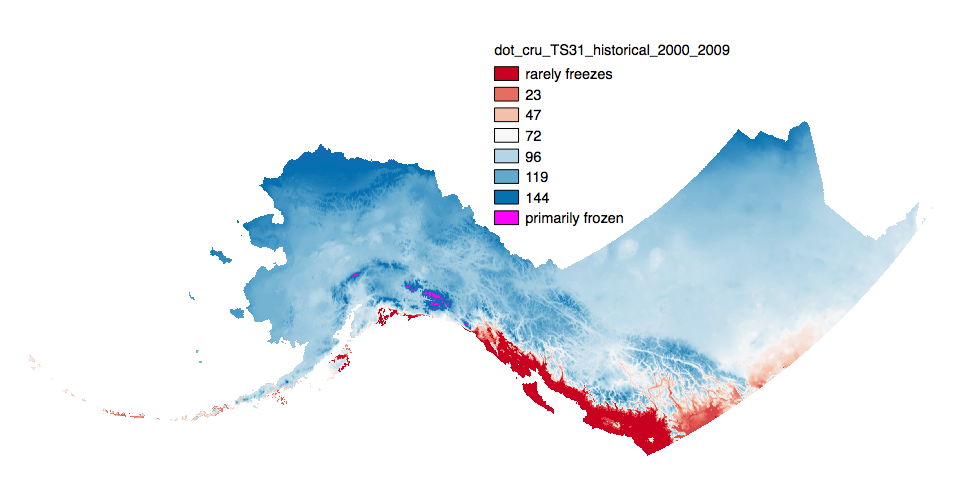
This set of files includes downscaled historical estimates of decadal means of annual day of freeze or thaw (ordinal day of the year), and length of growing season (numbers of days, 0-365) for each decade from 1910 - 2006 (CRU TS 3.0) or 2009 (CRU TS 3.1) at 2x2 kilometer spatial resolution. Each file represents a decadal mean of an annual mean calculated from mean monthly data. **Day of freeze or thaw units are ordinal day 15-350 with the below special cases.** *Day of Freeze (DOF)* `0` = Primarily Frozen `365` = Rarely Freezes *Day of Thaw (DOT)* `0` = Rarely Freezes `365` = Primarily Frozen *Length of Growing Season (LOGS)* is simply the number of days between the DOT and DOF. ---- The spatial extent includes Alaska, the Yukon Territories, British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. Each set of files originates from the Climatic Research Unit (CRU, http://www.cru.uea.ac.uk/) TS 3.0 or 3.1 dataset. TS 3.0 extends through December 2006 while 3.1 extends to December 2009. **Day of Freeze, Day of Thaw, Length of Growing Season calculations:** Estimated ordinal days of freeze and thaw are calculated by assuming a linear change in temperature between consecutive months. Mean monthly temperatures are used to represent daily temperature on the 15th day of each month. When consecutive monthly midpoints have opposite sign temperatures, the day of transition (freeze or thaw) is the day between them on which temperature crosses zero degrees C. The length of growing season refers to the number of days between the days of thaw and freeze. This amounts to connecting temperature values (y-axis) for each month (x-axis) by line segments and solving for the x-intercepts. Calculating a day of freeze or thaw is simple. However, transitions may occur several times in a year, or not at all. The choice of transition points to use as the thaw and freeze dates which best represent realistic bounds on a growing season is more complex. Rather than iteratively looping over months one at a time, searching from January forward to determine thaw day and from December backward to determine freeze day, stopping as soon as a sign change between two months is identified, the algorithm looks at a snapshot of the signs of all twelve mean monthly temperatures at once, which enables identification of multiple discrete periods of positive and negative temperatures. As a result more realistic days of freeze and thaw and length of growing season can be calculated when there are idiosyncrasies in the data.
-
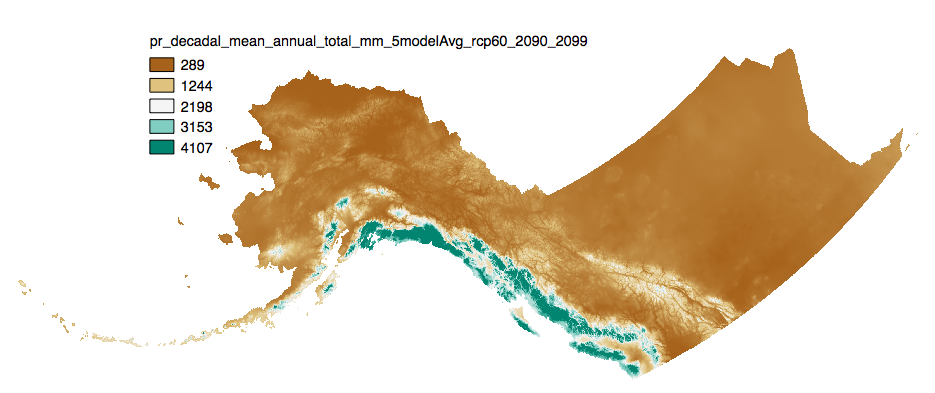
This set of files includes downscaled projections of monthly totals, and derived annual, seasonal, and decadal means of monthly total precipitation (in millimeters, no unit conversion necessary) from Jan 2006 - Dec 2100 at 2km x 2km spatial resolution. Each set of files originates from one of five top ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RPCs, or is calculated as a 5 Model Average. The downscaling process utilizes PRISM climatological datasets from 1961-1990. **Brief descriptions of the datasets:** Monthly precipitation totals: The total precipitation, in mm, for the month. For Decadal outputs: 1. Decadal Average Total Monthly Precipitation: 10 year average of total monthly precipitation. Example: All January precipitation files for a decade are added together and divided by ten. 2. Decadal Average Seasonal Precipitation Totals: 10 year average of seasonal precipitation totals. Example: MAM seasonal totals for every year in a decade are added together and divided by ten. 3. Decadal Average Annual Precipitation Totals: 10 year average of annual cumulative precipitation. For seasonal means, the four seasons are referred to by the first letter of 3 months making up that season: * `JJA`: summer (June, July, August) * `SON`: fall (September, October, November) * `DJF`: winter (December, January, February) * `MAM`: spring (March, April, May) Please note that these maps represent climatic estimates only. While we have based our work on scientifically accepted data and methods, uncertainty is always present. Uncertainty in model outputs tends to increase for more distant climatic estimates from present day for both historical summaries and future projections.
-
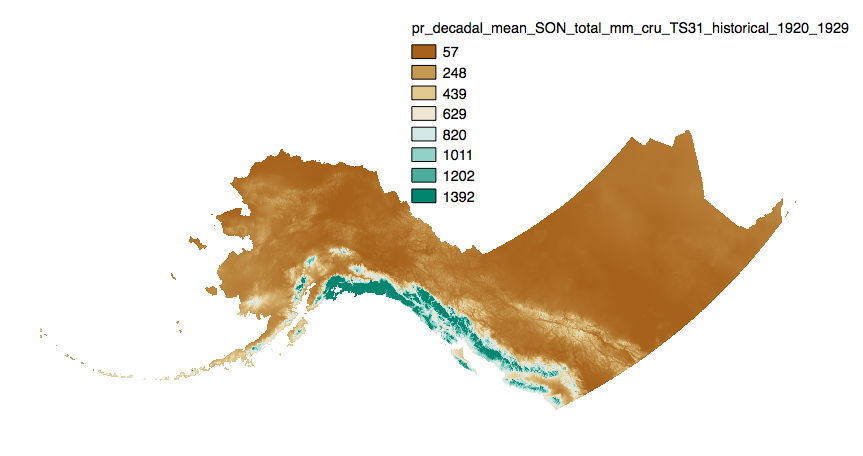
This dataset includes downscaled historical estimates of monthly average, minimum, and maximum precipitation and derived annual, seasonal, and decadal means of monthly total precipitation (in millimeters, no unit conversion necessary) from 1901 to 2006 (CRU TS 3.0), 2009 (CRU TS 3.1), 2015 (CRU TS 4.0), 2020 (CRU TS 4.05), or 2023 (CRU TS 4.08) at 2km x 2km spatial resolution. CRU TS 4.0 is only available as monthly averages, minimum, and maximum files. CRU TS 4.05 and 4.08 data are only available as monthly averages. The downscaling process utilizes PRISM climatological datasets from 1961-1990.
-
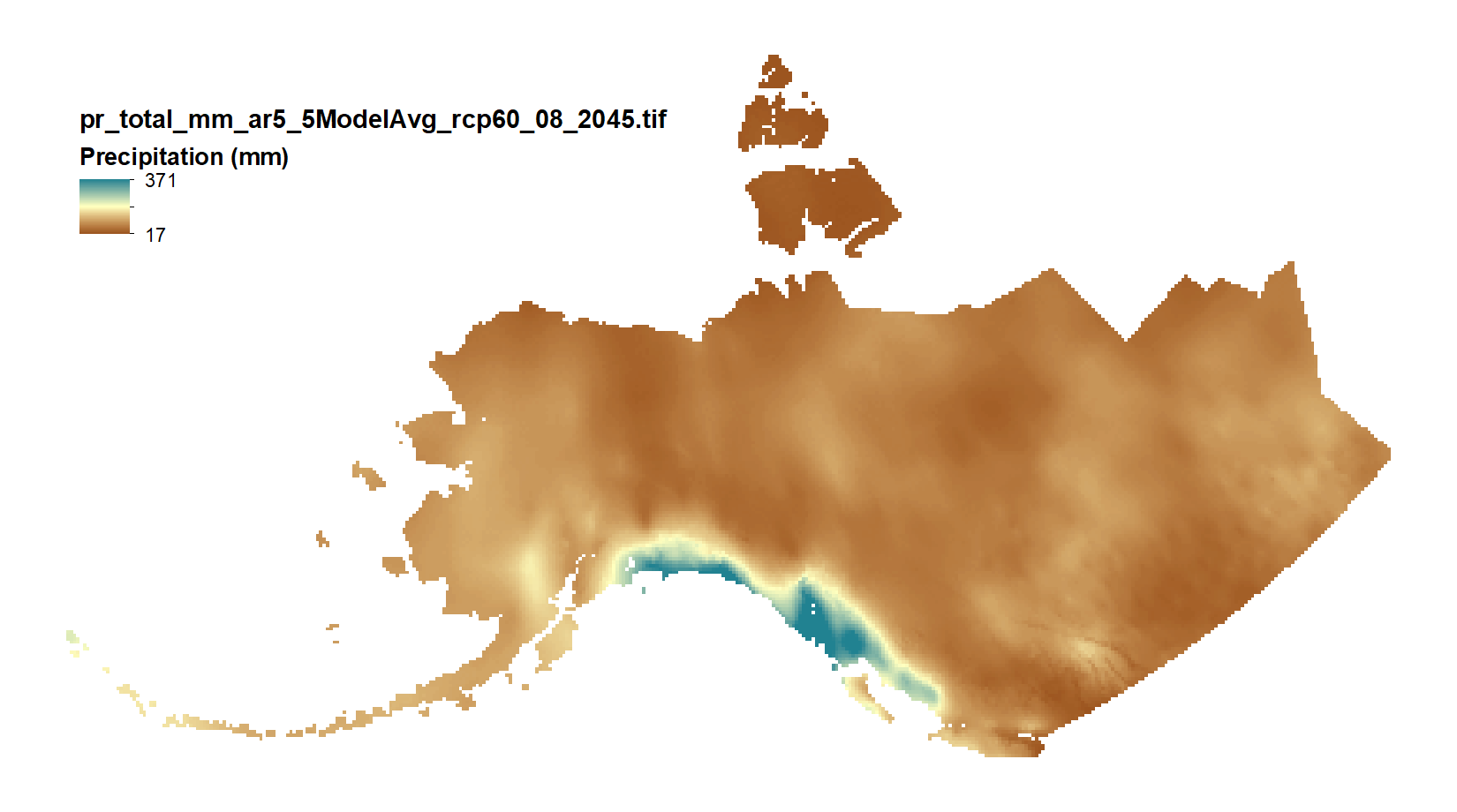
This set of files includes downscaled projected estimates of monthly total precipitation (in mm, no unit conversion necessary) from 2006-2300 (or 2006-2100, as some datasets from the five models used in modeling work by SNAP only have data going out to 2100) at 15km x 15km spatial resolution. They include data for Alaska and Western Canada. Each set of files originates from one of five top ranked global circulation models from the CMIP5/AR5 models and RPCs, or is calculated as a 5 Model Average. The downscaling process utilizes CRU CL v. 2.1 climatological datasets from 1961-1990 as the baseline for the Delta Downscaling method. Please note that these maps represent climatic estimates only. While we have based our work on scientifically accepted data and methods, uncertainty is always present. Uncertainty in model outputs tends to increase for more distant climatic estimates from present day for both historical summaries and future projections.
 SNAP GeoNetwork
SNAP GeoNetwork